
Published in the United States of America by Cambridge University Press, New York Subject to statutory exception and to the provision of relevant collective licensing agreements, no reproduction of any part may take place without the written permission of Cambridge University Press.Ĭambridge University Press has no responsibility for the persistence or accuracy of urls for external or third-party internet websites referred to in this publication, and does not guarantee that any content on such websites is, or will remain, accurate or appropriate. Information on this title: This publication is in copyright. Graeme Mitchison is at the Medical Research Councils Laboratory for Molecular Biology inīiological sequence analysisProbabilistic models of proteins and nucleic acidsĬambridge, New York, Melbourne, Madrid, Cape Town, Singapore, So PauloĬambridge University PressThe Edinburgh Building, Cambridge CB2 8RU, UK One of the Principle Investigators at the Washington University Genome Sequencing Center.Īnders Krogh is a Research Associate Professor in the Center for Biological SequenceĪnalysis at the Technical University of Denmark. Sean Eddy is Assistant Professor at Washington Universitys School of Medicine and also Richard Durbin is Head of the Informatics Division at the Sanger Centre in Cambridge, It presents the state-of-the-art in this important, new and rapidly developing Written by an interdisciplinary team of authors, the book is accessible to molecularīiologists, computer scientists and mathematicians with no formal knowledge of each Hidden Markov models, multiple alignment, prole searches, RNA secondary structureĪnalysis, and phylogenetic inference are treated at length.
This book provides the rst unied, up-to-date, and tutorial-level overview of sequenceĪnalysis methods, with particular emphasis on probabilistic modelling. Of sequence families, and the inference of phylogenetic trees using maximum likelihood

Hidden Markov models as the basis for prole searches to identify distant members Examples of such methods include the use of probabilisticallyĭerived score matrices to determine the signicance of sequence alignments, the use of Many of the most powerful sequence analysis methods are now based on principles
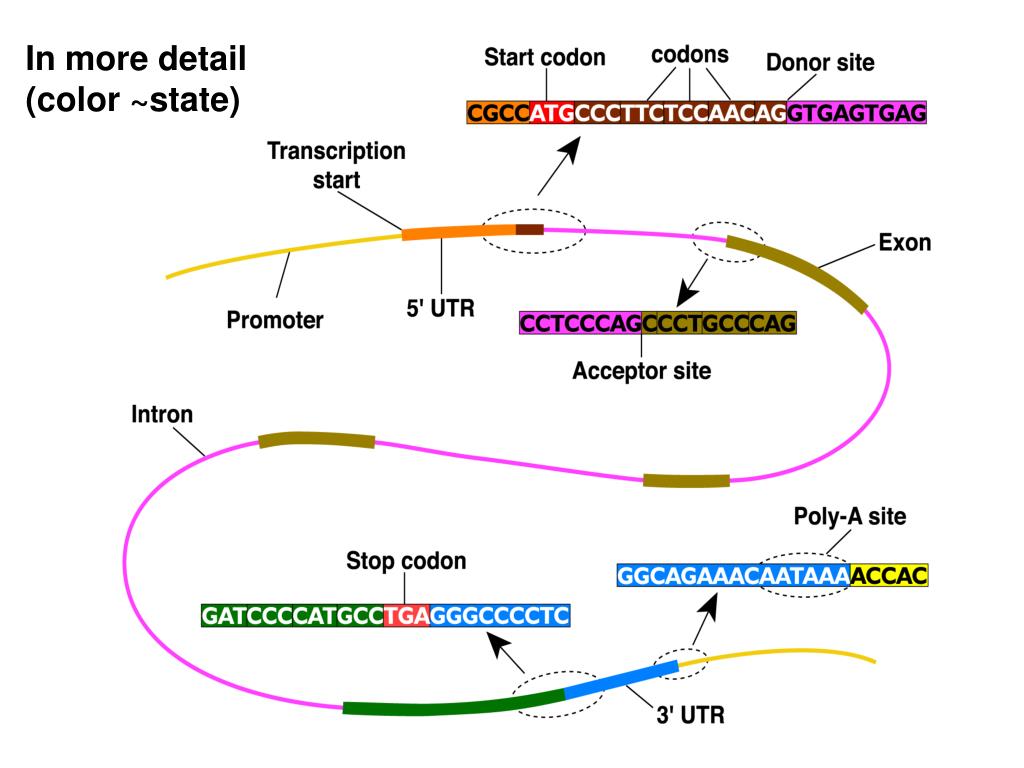
Research area of computational molecular biology, or bioinformatics. Of biological sequences are driving forward the newly-created and explosively expanding Understand the data is becoming ever more pressing. Human Genome Project which are producing an immense amount of data. The face of biology has been changed by the emergence of modern molecular genetics.Īmong the most exciting advances are large-scale DNA sequencing efforts such as the Probabilistic models of proteins and nucleic acids


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
